Dr. Eric Venn-Watson’s Highlights
-
The endocannabinoid system is a series of receptors located all over your body, responsible for certain homeostatic functions like pain regulation.
Stimulating the endocannabinoid system with endogenous cannabinoids can help with pain management.
Taking a supplement, like fatty15, can help your body synthesize more of the second-ever discovered fully-acting endocannabinoid, pentadecanoylcarnitine (PDC).
Pain can be tricky, especially if it sticks around longer than it should. Normally, pain is an indication that helps us decide what to do or not to do. Should we remove our hand from a hot pan? Should we continue to run on a sprained ankle?
When pain lasts longer than normal, however, it becomes unuseful and can even be detrimental to our overall health.
Understanding how our body feels pain and how we can manage it is crucial to help alleviate that pain and treat any of its underlying causes. Let’s explore how the body understands and responds to pain, how the endocannabinoid system plays a role, and what we can do to get relief.
Understanding Pain
Pain hurts, and usually, that hurting sensation signals us to remove ourselves from a dangerous situation or stop a certain activity.
There are two main types of pain: chronic pain and acute pain.
- Chronic pain. This is pain that lasts longer than three months. It isn’t beneficial to your body because it usually doesn’t indicate an injury, and can even lead to depression or anxiety. Chronic pain is often associated with inflammation in the body and can sometimes be due to a disease or autoimmune disorder, but can also be due to a injury that hasn’t (and won’t) fully heal.
- Acute pain. This is temporary pain, like the kind you feel when you sprain an ankle or cut your finger. You may have pain in the area of the injury for a few months at most while the injury heals, and that pain serves as a reminder that it isn’t safe to resume normal activity just yet.
Your brain processes pain through a series of receptors located all over the body that collect data and send it back to the brain. These receptors are located on nerves that sense injury or imbalance and send the data back to the control center.
The control center understands the need for corrective action and signals changes to be made to heal or alleviate the pain.
What Parts of the Brain Are Involved With Pain?
Several parts of the brain are involved with pain perception: the primary somatosensory cortex, secondary somatosensory cortex, prefrontal cortex, amygdala, thalamus, cerebellum, and anterior cingulate cortex.
In each of these parts of the brain, special receptors in the endocannabinoid system work to regulate the feeling of pain and help us find relief.
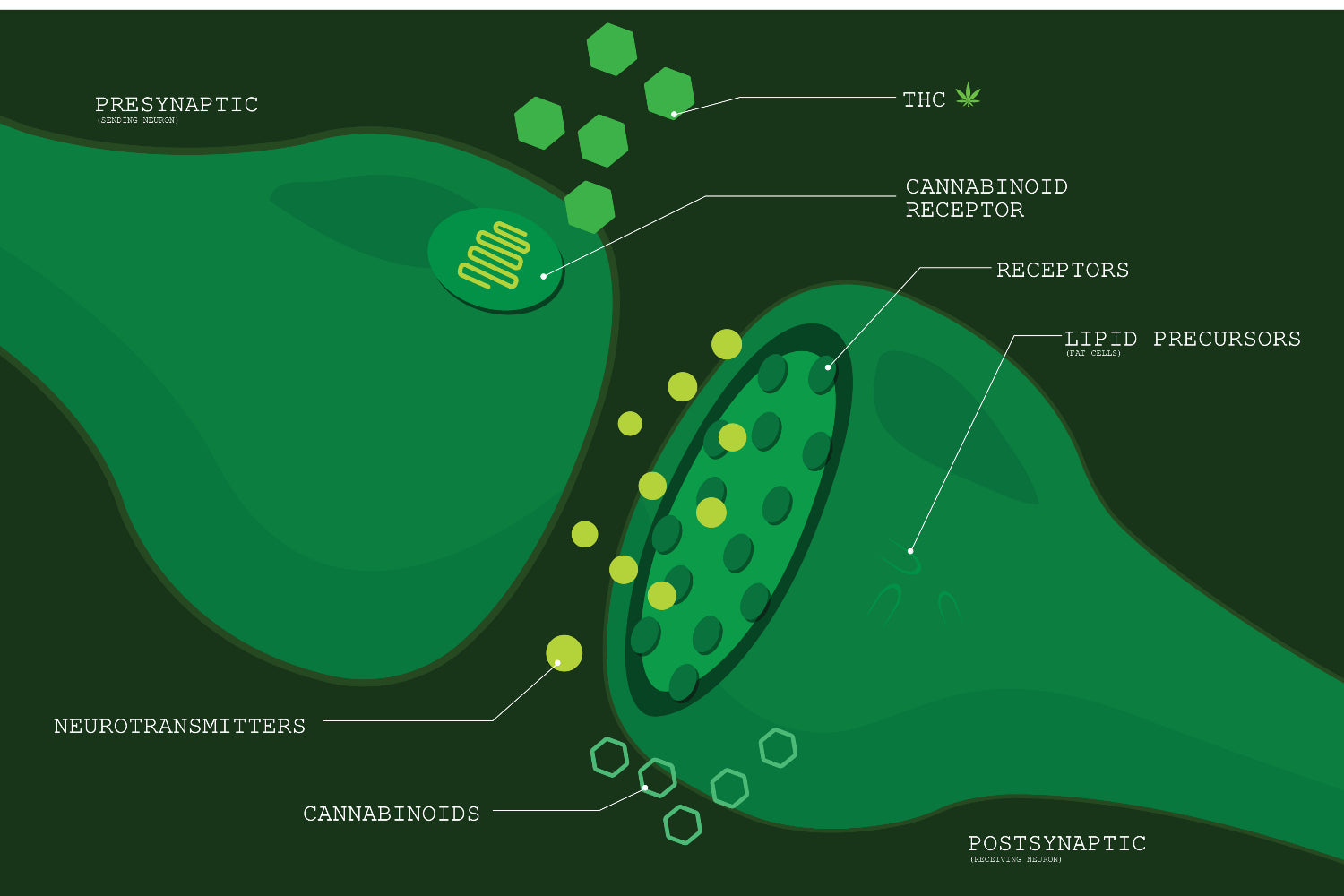
What Is the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system is made up of three important parts:
- Receptors
- Endocannabinoids
- Enzymes
These three parts work together to help keep the body in balance by regulating functions like sleep, body temperature, mood, memory, appetite, and pain. As we learn more about the endocannabinoid system, we can learn how to engage it and use it therapeutically in the treatment of pain, the regulation of sleep, and other ways to help keep us balanced and sharp.
Receptors
There are two types of receptors in the ECS: CB1 receptors and CB2 receptors.
- CB1 receptors are located primarily in the brain and spinal cord and aid in the regulation of sleep, mood, body development, pain, memory, and cognitive function. These receptors are less plentiful than CB2 receptors.
- CB2 receptors are located in our immune tissue and digestive system and help with both immunity and digestion. CB2 receptors are located in the peripheral nervous system.
Activating these receptors can help bring regulation to the functions they control. And activating them takes endocannabinoids.
Enzymes
Your body needs enzymes to break down endocannabinoids that have been used. This is why enzymes are crucial to the endocannabinoid system. Once the body has used an endocannabinoid, an enzyme plays clean up, breaking it down and making sure it is eliminated from your body.
The fatty acid hydrolase breaks down the endocannabinoid AEA, and monoacylglycerol acid lipase breaks down 2-AG. These are necessary for the functioning of the endocannabinoid system.
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids are compounds made by your body that interact with your CB1 and CB2 receptors. Until recently, we were only aware of two: anandamide (AEA) and 2-AG.
- Anandamide. This is also known as the bliss molecule and was the first ever endocannabinoid to be discovered. It interacts and stimulates only CB1 receptors..
- 2-AG. This is the first fully-acting endocannabinoid, which means it can interact with both CB1 and CB2 receptors. The fact that this endocannabinoid is fully acting means we can get more benefits from it.
Until very recently, it was thought that only these two endocannabinoids existed in the body. Now, we are aware of a third, and it’s the second ever discovered fully-acting endocannabinoid.
A note about cannabinoids: while we produce our own cannabinoids internally (called endocannabinoids), there are plant-based cannabinoids called phytocannabinoids that can also interact with the receptors located in our internal endocannabinoid system. You’re probably familiar with CBD and THC, both phytocannabinoids from the cannabis sativa plant. These also affect our ECS, however our CB1 and CB2 receptors were not created to use phytocannabinoids. Rather, these receptors are best activated by our own body balancing, homeostasis inducing endocannabinoids.
What Is PDC?
Researchers studying the long-term benefits of a particular essential fatty acid, known as C15:0, found another unexpected benefit of this essential, odd-chain, saturated fat: it helps our bodies synthesize pentadecanoylcarnitine or PDC. This fully-acting endocannabinoid can help stimulate both CB1 and CB2 receptors.
How PDC Is Made
Your body needs fatty acids to make endocannabinoids, and PDC is synthesized using C15:0. C15:0 is now accepted as the first essential fatty acid to have been discovered since the omegas over 90 years ago. An essential fatty acid is one that our bodies don’t readily make and thus, we must get the nutrient from our diet.
Where C:15 Comes From
C15:0 is found primarily in full fat dairy products. However, simply increasing your intake of whole fat dairy would also mean ingesting extra calories and the bad, proinflammatory, even-chain saturated fats. Therefore, getting C15:0 in the form of a dietary supplement may be a good choice.
Elevate your cells. Elevate your self.
Buy NowFatty15
Fatty15 is a breakthrough supplement born from scientific discovery, containing one pure ingredient, FA15™. This vegan-friendly, sustainably-produced, award-winning version of C15:0 contains just 100 mg and is enough to restore your circulating levels of C15:0, so your body can make more PDC and help stimulate the receptors in your endocannabinoid system.*
Unlike other fatty acid supplements (like omega-3), C15:0 has no fishy aftertaste and is not prone to oxidation and going rancid like omega-3, fish oils are. Speaking of omega-3, fatty15 was compared head-to-head with the purest, most effective form of omega-3 (pure EPA), and the results might surprise you.
Fatty15 vs. Omega-3
When compared against omega-3, fatty15 was found to be broader, better, and safer:*
- Broader. Fatty15 had 26 more dose-responsive benefits than omega-3. It also helped stop bad cells from proliferating.
- Better. Out of 12 damaged cell types studied, fatty15 could repair 10 of them. Omega-3 could only safely repair four.
- Safer. Fatty15 was found to be safe for all 12 cell types. Omega-3 was toxic to four cell types at clinically relevant doses, including lung and blood vessel cells.
Further, omega-3 can lead to side effects like thinning of the blood, easy bruising, and low blood pressure. Not to mention the unavoidable fishy aftertaste that most fish oil supplements are known for.
Fatty15 also supports the way your cells communicate with each other. By naturally binding to receptors located all over the body called PPARs, it can help bring functions like sleep, mood, and appetite back into balance.*
Get Fatty, Find Balance
Stimulating your CB1 and CB2 receptors through the use of your body’s own endocannabinoids can help regulate many functions in your body, including pain. Fatty15 supports the synthesis of PDC, a fully-acting endocannabinoid that is an important part of your endocannabinoid system.*
In addition, fatty15 benefits your cellular health and your overall health and wellness.* Further, C15:0 (the only ingredient in fatty15) has been repeatedly associated with improved metabolic, immune, liver and heart health.*
Looking to learn more about fatty15? Check out the science of C15:0 here.
Ready to get started for yourself? Give fatty15 a try for yourself here.
Sources:

Eric Venn-Watson M.D.
CEO, Co-Founder
Senior Scientist, Co-Founder
Eric is a physician, U.S. Navy veteran, and Co-founder and COO of Seraphina Therapeutics. Eric served over 25 years as a Navy and Marine Corps physician, working with the special forces community to improve their health and fitness. Seraphina Therapeutics is a health and wellness company dedicated to advancing global health through the discovery of essential fatty acids and micronutrient therapeutics.
You May Also Like...
The Ultimate Guide to Cellular Longevity Supplements for Optimal Health
Introduction to Cellular Longevity and Supplementation
Cellular longevity is the science of maintaining your cells’ optimal structure and function over time—a cornerstone for healthy aging and overall well-being. As we age, our cells face mounting stress, slower repair, and increased...
Cellular Health Supplements: The Importance of C15
Cellular health has flown into the spotlight recently, but if you’re confused about it, chances are you probably aren’t taking care of your cells as best as you can. Cellular health refers to the health and function of every...


