Dr. Eric Venn-Watson’s Highlights
-
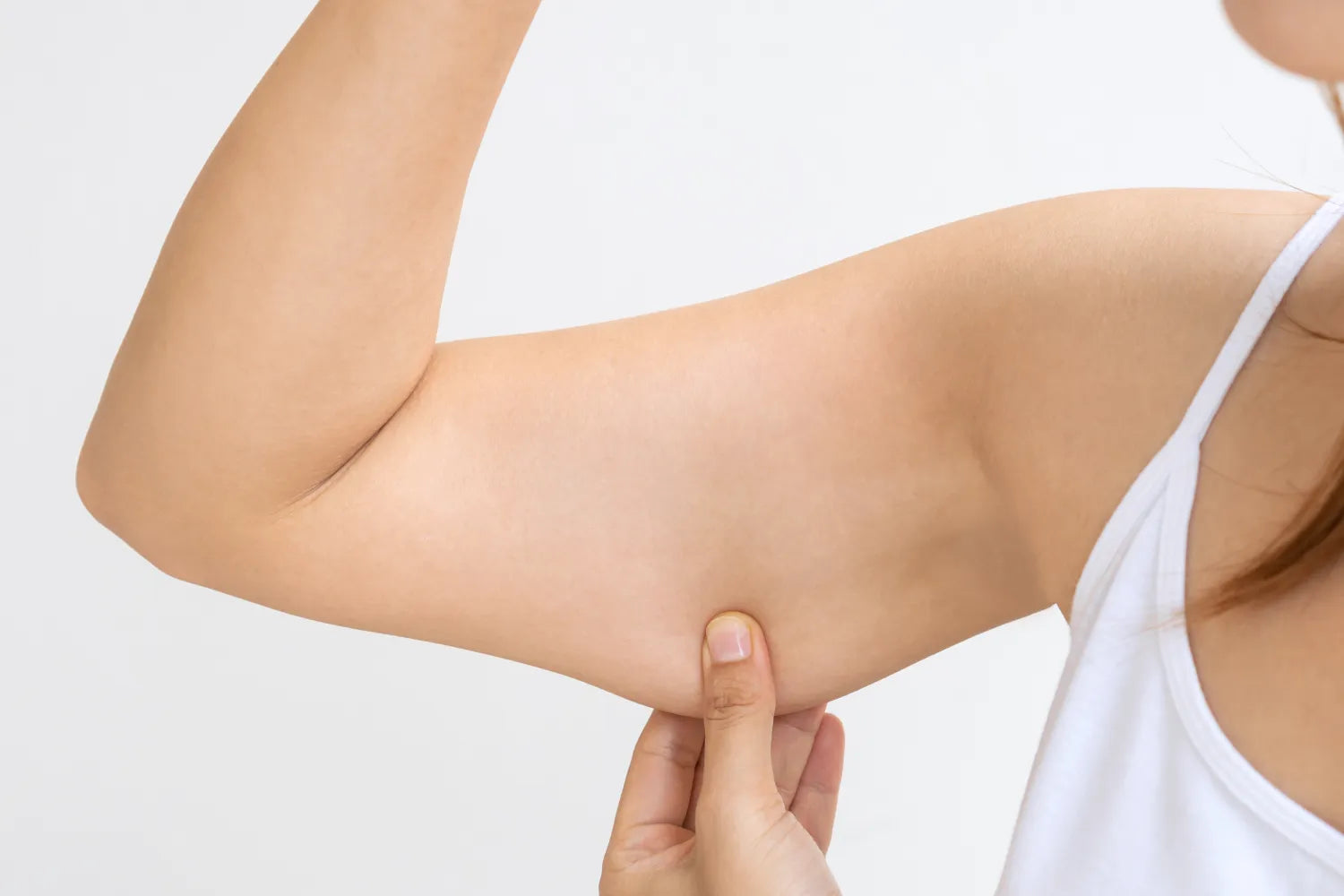
Sagging skin can be caused by sun exposure, the natural aging process, and a lack of essential nutrients.
Although dietary deficiencies are rare, addressing them (if you have them) may help support the look and appearance of your skin.One newly discovered dietary deficiency affects as many as one in three people worldwide, and fixing it can support your skin, healthspan, and longevity.
The skincare market is massive. Globally, it reached $109 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow by an additional $100 billion in 2024. It isn’t surprising because the skin, the largest organ of our bodies, is often the first place we notice the visible signs of aging.
Sagging skin, skin that lacks luster, and skin that doesn’t feel as firm as it used to can lead us down aisles of skincare products that promise to lift, tighten, and restore our skin to its youthful appearance. The problem is that, in some respects, we’re fighting an uphill battle.
The natural aging process changes the way our skin looks and feels. Years of sun damage can leave us with spots, discoloration, and even skin cancer. The good news is that we can care for our skin in proactive ways. One way is to determine if our skin is suffering due to a deficiency in our diets.
Although dietary deficiencies are rare, it is possible that underlying illness or extremely restrictive diets can leave a person missing a key nutrient that is known for supporting the skin. We’ll look at which nutrients and vitamins can lead to sagging skin and how you can fix it.
We’ll also talk about the most recently discovered nutrient deficiency and how it affects not only your skin but your entire body. Don’t worry — we’ve got a solution for that, too.
What Causes Sagging Skin?
Sagging skin can be caused by several different factors. We can work to prevent some of them, but others are simply the result of getting older and experiencing naturally occurring changes over time.
Loss of Collagen and Elastin
The number one reason our skin begins to lose firmness and elasticity is due to the reduced production of two proteins in the skin, collagen and elastin. Collagen is responsible for keeping our skin plump and tight, while elastin helps give our skin the ability to snap back into place when it is stretched.
The skin naturally begins to slow the production of collagen and elastin as we get older. We produce about one percent less collagen and elastin each year starting at age 20. Less collagen production means our skin is less firm and elastic than it was in our youth.
Loss of Fat
Another reason the skin begins to sag is due to an overall loss of fat in the face. With age, the fat pads in the face begin to shrink.
Fat in the face may also be redistributed to different areas, like the jowls or the chin, instead of underneath the eyes and in the hollows of the cheeks, where it is located in more youthful skin. This can also cause the skin to hang on cheekbones and appear to sag beneath the eyes.
Weight Loss
Losing weight can lead to sagging skin. The faster you lose weight, the more likely you are to experience skin sagging. People who have had weight loss surgery are particularly at risk of skin sagging due to the rapid weight loss they may experience after their surgery.
Sun Damage
By now, we know that sun exposure can damage our skin and lead to premature aging. It’s also one of the primary causes of hyperpigmentation. UV radiation from the sun breaks down elastin fibers in the skin, causing skin elasticity to decline. The sun also causes skin cells to produce free radicals, which harm healthy cells and lead to skin aging.
Vitamin Deficiencies
Essential vitamins and minerals play a role in healthy skin. If you are on a restrictive diet or have an underlying illness that causes poor vitamin and mineral absorption, you may suffer from one of these deficiencies.
Which Vitamin Deficiency Causes Skin Sagging?
Healthy people in the United States rarely suffer from vitamin deficiencies. Access to fresh and fortified foods has virtually eliminated dietary deficiencies. However, if you are experiencing skin sagging that seems sudden, your diet could be the culprit. Some vitamins and minerals can cause your skin to appear dull and even dehydrated.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is an essential vitamin that helps with the immune system, iron absorption, cognitive function, and tissue growth and repair. One tissue it helps produce and repair is collagen.
Collagen synthesis requires vitamin C, and if you are deficient in vitamin C, you may begin to notice changing skin conditions. Vitamin C is also a powerful antioxidant that can help protect the skin from free radicals.
Lack of vitamin C may first be noticeable by:
- Dry skin, or dryness in areas of skin that are normally oily
- Slower wound healing
- Areas of itchy, flaky skin (sometimes referred to as eczema)
- Sagging skin
The only way to find out if you have a vitamin C deficiency is to have a blood test. If you are deficient and the source of the deficiency is not due to a dietary restriction, you may need to consider taking a vitamin supplement to help ensure you are getting enough vitamin C in your body.
If your diet doesn’t consist of many citrus fruits, a dietary adjustment may help you notice an improvement in your skin health.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is another essential vitamin that plays an important role in healthy skin. Vitamin E can help with skin hydration and help strengthen the skin barrier. The application of topical vitamin E creams in your skincare routine is often recommended by dermatologists to help reduce the visible signs of pigmentation issues.
A deficiency in vitamin C may cause your skin to appear dull, dry, and possibly saggy. A blood test is needed to determine if you are deficient in vitamin E. If you are, you can add nuts, seeds, leafy greens, and avocados to your diet.
Although these vitamin deficiencies could lead to visibly sagging skin, it’s more likely that sagging skin is the result of the aging process. There are two ways the body ages, and one of those ways is reversible.
Aging in Reverse
We age in two different ways: chronologically and biologically. Chronological aging is the age we are because of our birthdays. As such, we can’t change it. Biological aging, however, is the age of our cells, which can be younger or older than our chronological age.
Aging happens in our cells. Researchers have identified 12 key ways in which our bodies age as the result of cellular processes. These 12 hallmarks of aging can make us age faster or slower than our chronological age, depending on our genetics, lifestyle factors, and how well we take care of ourselves.
Now for the best news: Biological aging can be reversed. By biohacking our biological age, we can improve our healthspan, increase our longevity, and even see positive outcomes in our skin health.
One way to biohack your body is by increasing the amount of a newly discovered as essential fatty acid in your diet.
C15:0: The Longevity Secret
It happened by chance. Researchers studying longevity in bottlenose dolphins noticed that populations of these mammals with higher levels of a particular nutrient known as C15:0 had fewer occurrences of age-related diseases. They took their research further and discovered that these healthspan-protective benefits were available to humans, too.
As initially published in Nature Scientific Reports in 2020, C15:0 has been shown to reverse aging inside human cells. Since that initial publication, there are now over 100 peer-reviewed publications describing the health benefits of C15:0. As an essential fatty acid, C15:0 is critical for our bodies as it actively repairs, restores and revitalizes our long-term health at the cellular level by:*
- Strengthening our cell membranes (and us) against age-related breakdown
- Repairing mitochondrial function, which keeps our body’s energy-producers going
- Naturally activating receptors (including PPARs and AMPK) that regulate our metabolism, immunity, mood, sleep, and appetite
- Naturally inhibiting damaging pathways (including mTOR and JAK-STAT) as a means to support longevity
All in, C15:0 provides 36+ cellular benefits to support our long-term health and longevity, which is better than three leading longevity-enhancing molecules: rapamycin, metformin, and acarbose.
Cellular Fragility Syndrome: The Newest Deficiency on the Block
Additionally, C15:0 has another superpower: It prevents and treats Cellular Fragility Syndrome, a newly discovered nutrient deficiency associated with low levels (< 0.2%) of C15:0, that may be affecting 1 in 3 people globally.
Cellular Fragility Syndrome is consistently associated with negative health conditions like:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease
- Liver disease NAFLD
Cellular Fragility Syndrome results in a process known as ferroptosis, which is a type of cellular death linked to accelerated aging, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and NAFLD. C15:0 is a strong, stable fatty acid that keeps our cell membranes strong (and our cells healthy) and protects them from ferroptosis.
What Is C15:0?
C15:0 is an odd-chain, saturated fatty acid that is present in trace levels in whole-fat dairy products and some plants and fish. C15:0 is the first essential fatty acid to be discovered in almost 100 years since omega-3.
Essential nutrients are those that our bodies don’t make but are necessary to maintain physiological health. We have to get C15:0 from our diets or through supplementation. Further, over 100 peer-reviewed studies have repeatedly shown that people with higher levels of this essential nutrient have better long-term metabolic, heart, and liver health.
How Do I Know if I’m Deficient?
A simple blood test can let you know if you are considered deficient. Low C15:0 levels under 0.2% of the total fatty acids in your red blood cell membranes can cause weakened cell membranes and Cellular Fragility Syndrome, increasing the risk of poor metabolic, heart, and liver health.
C15:0 levels between 0.2% and 0.4% are considered healthy and protect against the Cellular Fragility Syndrome. It’s worth pointing out that people who live in the Longevity Blue Zone of Sardinian Blue Zones (where residents consistently live to be older than 100) have average C15:0 levels of C15:0 levels that are much higher. In Sardinia, Italy, the average C15:0 level is 0.64%.
You can find out if you are deficient in C15:0 by having your healthcare provider obtain a fatty acid panel or by using this at-home test kit. This kit requires a finger-prick blood sample that is analyzed by a lab and will tell you whether or not you are deficient.
Additionally, you may see improvements in labs such as your complete blood panel, cholesterol panel, and liver enzymes. If you discover that your C15:0 levels are low, there’s a solution.
Optimize Your C15:0 Levels
Increasing your C15:0 levels through food intake alone is problematic. C15:0 is a naturally occurring odd-chain saturated fatty acid, with trace levels found in dairy fat, as well as some types of fish and plants.
Increasing your intake of whole dairy would mean packing in excess comes with a lot of calories, sugar (from lactose), and the bad, pro-inflammatory, even-chain saturated fats. It would also mean involving cows, which doesn’t make the mission vegan-friendly or environmentally conscious. A good solution is to supplement your diet with fatty15.
Fatty15 is the first and only supplement that contains the pure, vegan-friendly, award-winning version of C15:0 known as FA15™, making it the easiest way to restore your C15:0 levels and support your cells.
Optimize C15:0 Absorption
In milk (and other foods), C15:0 is attached to branches of lipids called triacylglycerides, AKA triglycerides. That means our gut has to use digestive enzymes to break down these triacylglycerides to release C15:0 as a free fatty acid.
Once C15:0 is released, it is ready to be absorbed. These steps make it less efficient for our bodies to absorb C15:0 from the foods we eat. Fatty15 contains pure C15:0 in its most bioavailable free fatty acid form, which makes it easy to absorb.
Decrease Your Calories
It’s no secret that whole-fat dairy packs in an awful lot of calories. One serving of whole milk contains about 150 calories, compared to just 80 calories in skim milk or 30 calories in plant-based milk. Adding additional calories to your diet may not be the best fit for maintaining your weight.
Fatty15 contains just one calorie.
Avoid the Cows
If you’re vegan, consuming animal products is off the table, which may make it harder for you to get the C15:0 your body needs. In addition, the movement to more plant-based milk has reduced population levels of C15:0 because plant milk does not contain any C15:0.
Fatty15 is made from plants and is vegan-friendly.
Elevate your cells. Elevate your self.
Buy NowFatty15: The C15:0 Solution
Your skin may show a little age, but with the help of fatty15, you can reverse cellular aging and enjoy looking and feeling biologically younger than your birthday.
Sources:
Skincare Market Size, Share, Trends | Growth Analysis [2032]
The role of elastin and collagen in cutaneous aging: intrinsic aging versus photoexposure | PubMed
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: What It Is & Its Effect on Your Skin | My Cleveland Clinic.com

Eric Venn-Watson M.D.
CEO, Co-Founder
Senior Scientist, Co-Founder
Eric is a physician, U.S. Navy veteran, and Co-founder and COO of Seraphina Therapeutics. Eric served over 25 years as a Navy and Marine Corps physician, working with the special forces community to improve their health and fitness. Seraphina Therapeutics is a health and wellness company dedicated to advancing global health through the discovery of essential fatty acids and micronutrient therapeutics.
You May Also Like...
What’s the Best Diet To Improve Longevity?
Want to live long and well? Discover the best diets for longevity, and how Fatty15™ supports cellular health for a longer, healthier life.
Cellular Health Supplements: The Importance of C15
Cellular health has flown into the spotlight recently, but if you’re confused about it, chances are you probably aren’t taking care of your cells as best as you can. Cellular health refers to the health and function of every...


